Navigating the Cyclical Fog: An In-Depth Analysis of Glyphosate's Price Trajectory and Seasonal Patterns from 2018-2024
The glyphosate market has experienced a spectacular "roller-coaster" ride over the past several years. To explore its future direction, we must first review its historical trajectory to identify underlying patterns and logic. By examining detailed monthly price data from 2018 to 2024, we can clearly outline its macro-cycles and inherent seasonal characteristics.
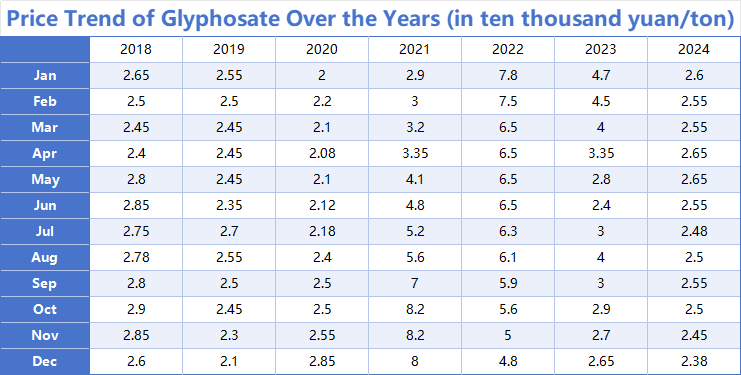
I. The Three Macro-Cyclical Phases
From a long-term perspective, the price trend of glyphosate from 2018 to 2024 can be divided into three distinct phases:
1. The Stable Bottoming-Out Period (2018-2020):
During this period, the market was relatively stable, with prices primarily fluctuating between 20,000 and 29,000 RMB/ton.
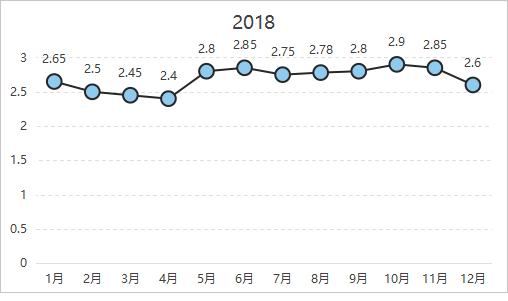
2018: The price exhibited a "W-shaped" trend of falling, rising, and then falling again. After hitting a low of 24,000 RMB/ton in April, it saw two rebound waves from April-June and August-October, peaking at 29,000 RMB/ton.
2019: The overall tone for the year was weak, with the price center of gravity shifting downward. Except for a significant rebound of 14.89% from June to July due to short-term supply-demand shifts, the price remained in a downward channel for the rest of the year, falling to 21,000 RMB/ton by year's end, highlighting a market characterized by oversupply and weak demand.
2020: The market began to brew a transformation. After hovering at a low of around 21,000 RMB/ton in the first half of the year, a strong upward trend began in June, with the price climbing back to 28,500 RMB/ton by December. This rally, driven by a surge in overseas demand, domestic supply constraints, and rising costs, set the stage for the epic market of the following year.
2. The Historic Surge Period (2021-2022):
In 2021, driven by a supply-demand imbalance, the glyphosate market entered an unprecedented phase of explosive growth, setting historical records.
2021: This was an "epic year" for glyphosate. The price skyrocketed from 29,000 RMB/ton at the beginning of the year to an astonishing peak of 82,000 RMB/ton in October and November. The core drivers were a severe global supply-demand mismatch, superinflation in raw material and energy costs, and market sentiment fueled by panic hoarding.
2022: From this high point, the market embarked on a long downward channel. Prices began to fall from an absolute high of 78,000 RMB/ton at the start of the year. Although there was a relatively stable period around 65,000 RMB/ton from March to July, it could not reverse the overall downward trend, and the price had retreated to 48,000 RMB/ton by year-end.
3. The Rapid Regression Period (2023-2024):
After the bubble was squeezed out and value was reshaped, the market began to accelerate its return to the historical mean.
2023: The price experienced a "cliff-like" drop. In the first half of the year, it plunged from 47,000 RMB/ton to 24,000 RMB/ton in June, wiping out most of the previous gains. Notably, the market saw a powerful rebound of 66.67% from June to August, with the price climbing back to 40,000 RMB/ton. However, this did not reverse the year's downward trend, and the price ultimately closed at 26,500 RMB/ton.
2024: The market entered a phase of low-level consolidation. Prices fluctuated within a narrow range of 23,800 to 26,500 RMB/ton throughout the year. This performance closely mirrored the historical platform of 2018-2019, signaling that the market had largely returned to rationality after experiencing dramatic ups and downs.
II. The Deeper Logic of Seasonal Patterns — A 'Counter-Demand' Price Game
A review of historical data reveals a seemingly paradoxical yet recurring cyclical feature: glyphosate prices often rise in the third quarter (Q3) but fall in the fourth quarter (Q4), which is typically anticipated as the peak demand season. (The unilateral surge in 2021 and the unilateral decline in 2022 are exceptions under special market conditions).
Behind this phenomenon lies a deep interplay between supply-demand expectations and reality:
Why Do Prices Rise in Q3? This period is not a traditional peak season for demand; the core logic for the price increase lies on the supply side. The high temperatures of summer are usually a routine maintenance period for factories, leading to lower operating rates and a tightening of actual market supply. At the same time, producers are still fulfilling previous orders, and although new orders are few, their overall production schedules remain full. This "tight supply" situation can easily trigger market concerns about scarcity, thereby pushing up price expectations and leading to a rally. The rebounds in June-August 2023 and August-September 2024 both validate this logic.
Why Do Prices Fall in Q4? Although the market generally holds optimistic expectations for the Q4 peak season, the reality is often a case of "strong expectations versus weak reality." After the annual AgroChemEx (ACE) exhibition in Shanghai in October, the actual procurement volume from downstream customers is frequently lower than anticipated. Meanwhile, upstream factories have completed their maintenance, and production capacity gradually recovers, stabilizing market supply. Under the dual pressure of "weaker-than-expected demand" and "recovering supply," market sentiment shifts from optimistic to cautious, and downward price pressure becomes the norm.
Looking back at the turbulent changes over the past seven years, the glyphosate market not only demonstrates long-term fluctuations driven by macroeconomic and industrial environments but also contains intrinsic seasonal patterns based on its operational characteristics. Currently, the market trend through 2024 seems to reaffirm this state of low-level fluctuation.
As the fourth quarter approaches, the market stands at a crossroads of historical patterns. Following the long-standing "Q4 decline" model, glyphosate prices may face downward pressure amid stable supply and yet-to-be-verified downstream demand. Of course, any historical pattern can be broken by new variables. The ultimate direction of the market will still require close attention to a combination of key factors, including the global macroeconomic environment, upstream raw material costs, environmental policies, and end-user agricultural demand. For industry participants, a profound understanding of this complete cycle and insight into the core logic of its seasonal dynamics is the key to navigating future uncertainties.


