Analysis of the Cucumber Crop Protection Technology Map: Strategic Choices Amidst Cyclical Registrations with Disease Control as the Core Battlefield
Introduction: A systematic deconstruction of the 409 pesticide products newly registered for use on cucumber in China over the past five years (2020-2024) provides clear insights into the technological evolution and strategic core of this market segment. The data reveals three prominent features shaping the overall landscape: first, a defense strategy with an absolute focus on fungal disease control; second, the parallel rise of bio-pesticides and precision-targeted chemical agents; and third, the dominance of environmentally friendly formulations, led by suspension concentrates. Together, these elements sketch out a new blueprint for cucumber crop protection that is green, precise, and subject to notable cyclical fluctuations.
I. The Core Battlefield: Disease Control is Paramount, with a Void in the Herbicide Market
Among all registered products, the most striking signal is the extremely uneven distribution of pesticide categories: fungicides account for a remarkable 253 products, comprising over 60% of the share, far surpassing insecticides (89) and plant growth regulators (41). This phenomenon profoundly reflects the primary pain point in cucumber production: economic losses caused by fungal diseases such as downy mildew, powdery mildew, and target spot are the core challenge currently faced by growers.
It is noteworthy that herbicide products are entirely absent from the registration list. This is not coincidental but is determined by the cultivation practices (e.g., plastic mulching, greenhouse cultivation) and biological characteristics of cucumbers. This indicates that weed management in cucumber cultivation relies more on physical and agronomic control methods, and chemical weeding is not a mainstream technical path in this sector, providing a clear market boundary signal for related enterprises.
II. Market Dynamics: A Significant "Peak-and-Trough" Registration Cycle
The number of registrations over the past five years has shown significant cyclical fluctuations, with two major peaks in 2021 (155) and 2024 (110), while 2022-2023 was a relative trough. This "peak-and-trough" phenomenon may be driven by several factors:
Product R&D Cycles: Corporate R&D pipelines for new products typically take several years, which can lead to a concentration of product approvals in specific years.
Market Demand Drivers: The outbreak of new and difficult-to-control pests and diseases may stimulate companies to accelerate the registration of targeted new products.
Policy and Regulatory Cycles: Adjustments in pesticide registration policies or the re-evaluation of specific active ingredients can also affect the pace of submissions and approvals.
Understanding this cyclicality is crucial for forecasting future competitive landscapes and the rhythm of new product launches.
III. The Technical Arsenal: Strategic Value of Three Representative Ingredients
Among the numerous active ingredients, three molecules from different classes stand out, each representing a key direction in current cucumber protection technology:
Kasugamycin: The "Evergreen" of Bio-Fungicides
As an antibiotic fungicide derived from microbial fermentation, Kasugamycin is heavily registered both as a single agent and in combinations (such as the classic pairing with Quinoline-copper). Its advantages lie in its unique mode of action (inhibiting protein synthesis), environmental friendliness, and low risk of resistance. Its frequent appearance fully reflects the strong market preference for green, safe, and bio-sourced solutions for cash crops like cucumber.
Flonicamid: The "Spearhead" for Precision Targeting of Sucking Pests
The high frequency of Flonicamid's registration, a selective insecticide with a novel mode of action, signals that cucumber insect control strategies are evolving towards precision and resistance management. It primarily targets difficult-to-control sucking pests like aphids and whiteflies by blocking their feeding behavior, making it relatively safe for non-target organisms and natural enemies. Its combination with neonicotinoids like Thiamethoxam is a typical resistance management strategy.
24-Epibrassinolide: The "Enabler" of Endogenous Plant Hormones
The large number of registrations for this type of plant growth regulator reflects a market demand that has upgraded from simple "pest and disease control" to a new stage of "enhancing crop stress resistance and quality." By regulating the balance of endogenous hormones, it can enhance the plant's resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses (like diseases, low temperatures, and drought) while improving fruit quality, making it a vital supplementary technology in modern intensive cultivation systems.
IV. Mainstream Tactics: The Revolution of Combination and Formulation
Combination Formulations—The Embodiment of Systematic Solutions:
With 209 registered products, combination formulations significantly outnumber single-agent products (150). This indicates that the market is no longer satisfied with "single-point strikes" but is pursuing "one spray, multiple effects" systematic solutions. For example, combinations like "Tetraconazole + Ethirimol sulfonate" are designed to simultaneously control multiple key fungal diseases, enhancing control efficiency.
The Formulation Revolution—The Overwhelming Dominance of Suspension Concentrates (SC):
Suspension concentrates, with 187 registrations, account for nearly half of all formulations. Their dominance stems from a combination of high efficacy, safety, and environmental friendliness. As a water-based formulation, it not only ensures uniform coverage and efficient penetration of the spray on cucumber leaves and fruits but, more importantly, it significantly reduces the use of organic solvents, perfectly aligning with the green development trend where low- and slight-toxicity products are the absolute majority (396/409).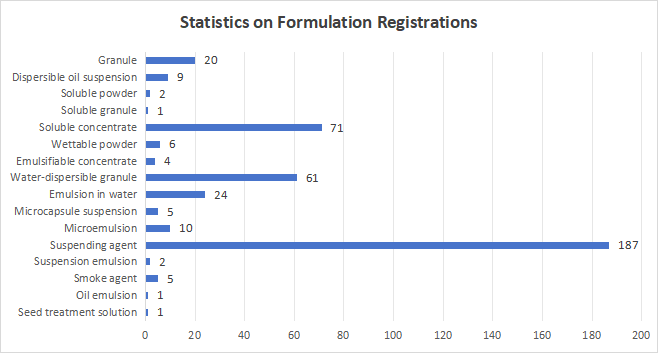
Conclusion and Outlook:
The technology map of cucumber pesticide registrations over the past five years clearly shows that the market is advancing towards a high-quality development stage with integrated disease management at its core, powered by the twin wings of bio-pesticides and precision chemical agents, and carried by green, environmentally friendly formulations. Future competition will no longer be a contest of single ingredients but will test a company's ability to provide integrated solutions that combine efficient disease control, precise insect management, and crop health conditioning. For agrochemical companies, deeply understanding this trend and positioning their product lines and technological innovations accordingly will be the key to winning in the future market.


